Understanding Electric Motors
Basics of Electric Motors
Electric motors are the silent workhorses powering countless aspects of modern life, from small household appliances to large industrial machinery. They operate on a simple yet fascinating principle: converting electrical energy into mechanical motion. It’s a dance of magnetic fields and electrical currents, orchestrated with precision and efficiency. When you consider the question, “what are electric motors and generators,” remember that these devices are fundamental to our energy ecosystem — each playing a vital role in transforming energy into useful work.
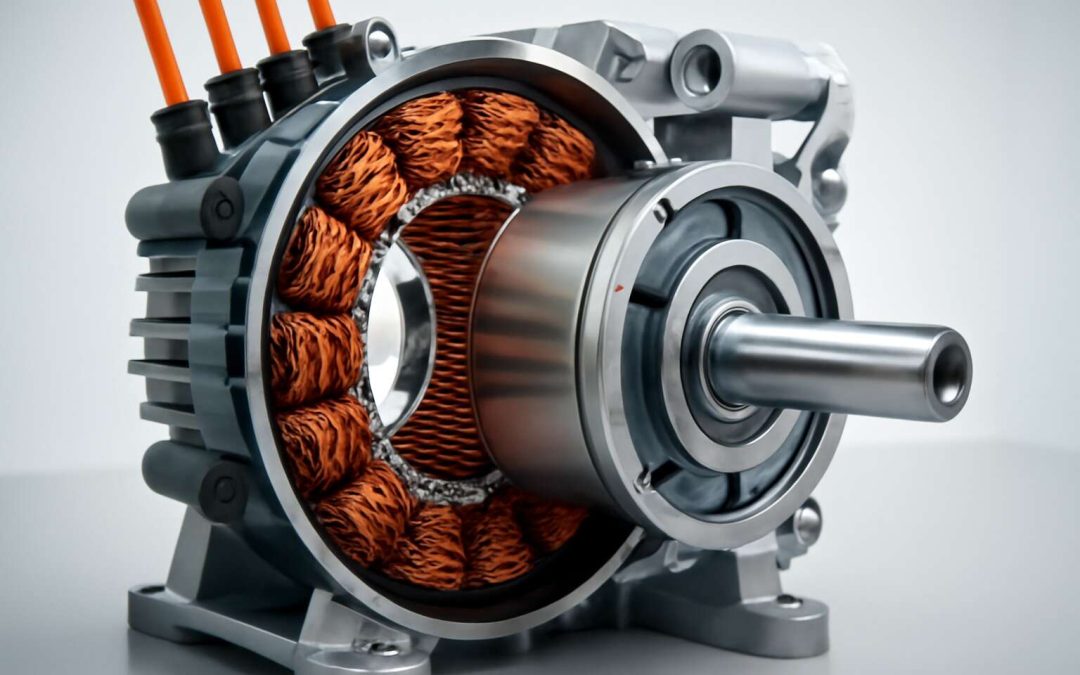
Understanding the basics of electric motors involves recognizing their core components: stators, rotors, and brushes, in many cases. These elements work together to generate motion through electromagnetic induction. Conversely, generators do the reverse—they convert mechanical energy back into electrical power, often harnessed from sources like turbines or engines. The seamless interplay between the two showcases their importance in both energy production and consumption. For example, in South Africa’s power landscape, electric generators are crucial for maintaining grid stability, while electric motors keep industries running smoothly.
How Electric Motors Work
Electric motors are the unseen forces driving our daily lives, transforming electric currents into motion with astonishing precision. They operate through a fascinating interplay of magnetic fields, where electricity energizes coils, creating a magnetic pull that spins the rotor. This process is the heart of what are electric motors and generators, revealing their dual nature—one converts electrical energy into mechanical power, the other does the reverse.
In essence, electric motors work by harnessing electromagnetic induction, often involving core components such as stators and rotors. When electric current flows through the stator coils, it generates a magnetic field that interacts with the rotor, causing it to turn. This movement powers everything from industrial equipment to household appliances, making electric motors indispensable in South Africa’s energy ecosystem.
Meanwhile, generators take this process a step further—they convert mechanical energy into electrical power, often from turbines or engines. This seamless transformation underscores their vital role in maintaining grid stability and powering industries. Understanding what are electric motors and generators provides a glimpse into the unseen machinery fueling modern progress.
- Stators and rotors working in harmony
- Electromagnetic induction at play
- Conversion between electrical and mechanical energy
Types of Electric Motors
Electric motors are as varied as the industries they power, each tailored to their unique demands and environments. When exploring what are electric motors and generators, understanding the different types reveals their remarkable versatility. From small, efficient brushed motors to the robust, maintenance-free brushless variants, each design embodies a different approach to electromagnetic transformation.
In South Africa, where energy needs are growing and sustainability is key, selecting the right motor is crucial. For instance, AC motors excel in industrial settings, providing reliable performance with simple design, while DC motors offer precise control for applications like electric vehicles or renewable energy systems. Recognizing these distinctions helps industries optimize their operations and harness the full potential of electrical machinery.
- Induction motors, renowned for their durability, are often the backbone of manufacturing plants.
- Permanent magnet motors deliver high efficiency—ideal for modern, eco-conscious innovations.
- Synchronous motors, with their ability to maintain consistent speed, are perfect for applications requiring exact timing and precision.
Understanding what are electric motors and generators involves appreciating these diverse types, each contributing uniquely to South Africa’s energy landscape and technological evolution.
Applications of Electric Motors
Electric motors breathe life into the machinery that powers South Africa’s bustling industries and innovative projects. Their applications are as diverse as the landscapes they serve, from the quiet hum of conveyor belts in mines to the precise movements of robotics in manufacturing. The question of what are electric motors and generators becomes essential when considering the seamless energy transformation that fuels progress.
In the realm of electric motor applications, versatility reigns supreme. For instance, induction motors, with their rugged durability, are the silent giants behind many manufacturing processes. Meanwhile, permanent magnet motors are fast becoming the choice for eco-conscious innovations, thanks to their high efficiency and minimal maintenance. Synchronous motors, known for their ability to maintain steady speeds, find a natural home in applications demanding unwavering precision.
Understanding these applications reveals how electric motors are woven into the fabric of modern South Africa—powering everything from renewable energy systems to transportation networks. They are not just machines but catalysts of change, embodying the dynamic spirit of technological evolution.
Understanding Electric Generators
Basics of Electric Generators
Electric generators are the silent giants powering our modern world, transforming motion into electricity with a touch of alchemical magic. Unlike electric motors, which convert electrical energy into mechanical motion, generators work in reverse—taking mechanical energy and producing electrical power. This fascinating dance of energy conversion is at the heart of countless industries, from renewable energy farms in South Africa’s wind corridors to backup power systems in bustling cities.
At their core, generators operate on the principle of electromagnetic induction. When a coil of wire spins within a magnetic field, it induces a flow of electric current—an invisible current that fuels homes, hospitals, and industries. This process is so vital that it has earned the title of the backbone of electricity generation worldwide. Understanding what are electric motors and generators reveals how seamlessly energy transforms, powering both our daily routines and the grand infrastructure of nations.
How Electric Generators Work
Understanding what are electric motors and generators reveals the elegant symmetry that underpins modern energy systems. At their essence, generators transform mechanical energy into electricity, harnessing the invisible power of electromagnetic induction. Picture a turbine spinning with relentless purpose—each rotation creating a magnetic flux that induces an electric current within coils of wire. This process is the heartbeat of electricity generation, powering entire cities and industries in South Africa and beyond.
In contrast, electric motors take the baton, converting electrical energy into mechanical motion. They operate on a simple yet profound principle: when electric current flows through a coil in a magnetic field, it experiences a force—producing movement. This energy conversion drives everything from manufacturing machinery to household appliances. Recognizing the fundamental differences and interconnected nature of these devices illuminates their crucial roles in both energy production and utilization.
For those interested in the mechanics, here’s a quick overview of the core processes involved in electric generators:
- Mechanical energy, often from turbines or engines, causes a coil or magnetic component to spin.
- This movement alters magnetic flux, inducing an electric current within stationary conductors.
- The generated electricity is then transmitted through power lines to homes and industries.
Such intricate energy dances not only define our technological landscape but also embody the ongoing quest for sustainable, reliable power in South Africa and around the world. The seamless interplay of what are electric motors and generators forms the backbone of our electrified existence, fueling progress and innovation at every turn.
Types of Electric Generators
Understanding the various types of electric generators reveals a fascinating array of designs, each tailored to specific needs and environments. These devices are not merely machines; they are the silent architects of our modern world, converting mechanical energy into electricity with remarkable precision. When exploring what are electric motors and generators, it becomes clear that the diversity of generator types reflects the complexity of our energy demands.
Among the most common are alternators, which provide reliable power for both industrial applications and renewable energy systems. There are also dynamos, historically pivotal in early electricity generation, and stationary generators that serve as backup power sources during outages. To better understand these variations, consider the following categories:
- AC Generators (Alternators): Produce alternating current, ideal for long-distance transmission and modern electrical grids.
- DC Generators: Generate direct current, often used in specialized applications such as electroplating or small-scale power needs.
- Portable Generators: Compact units delivering mobility and convenience for remote locations or emergency use.
Each type of electric generator exemplifies the ingenuity behind what are electric motors and generators — devices that underpin the very fabric of South Africa’s energy infrastructure. Their design intricacies and operational distinctions embody a broader philosophical reflection on how humanity harnesses nature’s forces, transforming them into the power that sustains our daily lives.
Applications of Electric Generators
Electric generators are the unsung heroes powering South Africa’s vibrant economy and everyday life. Their applications stretch far beyond simple backup power; they are essential in industries like mining, agriculture, and renewable energy projects. Understanding what are electric motors and generators helps us appreciate how these devices transform raw mechanical energy into the electricity that fuels our modern existence.
In the realm of electric generators, versatility is key. For instance, portable generators are invaluable during power outages or in remote locations, providing a reliable source of energy when grid access is limited. Meanwhile, large-scale AC generators—alternators—are the backbone of national power grids, ensuring millions of homes and businesses stay connected. Their ability to adapt to diverse environments underscores the importance of these machines in our daily routines.
- Powering remote communities where grid infrastructure is sparse.
- Supporting emergency response during natural disasters or grid failures.
- Driving renewable energy systems like wind turbines and solar farms, where efficient conversion of mechanical movement into electricity is vital.
By delving into what are electric motors and generators, we gain insight into their critical role in fostering resilience and innovation across South Africa. These devices are more than just technical marvels—they are the pulse of progress, enabling us to harness and channel energy in ways that shape our future.
Comparison Between Electric Motors and Generators
Principles of Operation
At the heart of modern energy systems, understanding the stark contrast between electric motors and generators reveals a fascinating dance of physics. While both devices revolve around electromagnetic principles, their core functions are almost mirror images—yet they operate with distinct purposes. Electric motors convert electrical energy into mechanical motion, powering everything from industrial machinery to household appliances. Conversely, generators take mechanical energy—often from turbines or engines—and transform it into electrical power. This fundamental difference underscores their respective roles in energy flow.
What are electric motors and generators? Their principles of operation hinge on the interplay between magnetic fields and electric currents. Electric motors utilize current-carrying conductors within magnetic fields to produce torque, causing rotation. Generators, on the other hand, harness mechanical rotation within magnetic fields to induce an electric current. To better grasp their relationship, consider this:
- The core principle of motors is electromagnetic induction causing motion.
- Generators reverse this process, converting motion into electrical energy through electromagnetic induction.
This elegant symmetry makes them essential, yet distinct, components in the energy landscape. Their seamless transition from one form of energy to another fuels industries across South Africa, shaping the future of sustainable power solutions.
Energy Conversion Processes
When it comes to energy conversion, electric motors and generators are like two sides of the same coin—one spins you into motion, the other pulls you out of it. But what exactly are electric motors and generators? At their core, they are marvels of electromagnetic engineering, transforming energy with a surprising elegance. Electric motors turn electrical energy into mechanical work—think of a conveyor belt or an electric vehicle—while generators do the reverse, transforming mechanical energy into electrical power, often fueling our homes or industries.
Their energy conversion processes are essentially mirror images, yet their roles couldn’t be more different. Electric motors use magnetic fields and electric currents to produce torque and rotation, energizing everything from small household appliances to massive industrial machines. Meanwhile, generators harness mechanical rotation—say, from a wind turbine or a diesel engine—and induce an electric current through electromagnetic induction. This fascinating symmetry is at the heart of modern power systems, including those powering South Africa’s energy infrastructure.
Main Uses and Applications
Understanding the distinction between electric motors and generators reveals a fascinating dance of energy transformation—each serving a vital role in our modern world. While they share similar principles rooted in electromagnetic induction, their main uses diverge sharply, reflecting the complex needs of society. Electric motors are the silent workhorses powering everything from household appliances to electric vehicles. They convert electrical energy into mechanical motion, making them essential for mobility and automation.
On the other hand, generators act as the backbone of electrical supply, especially in regions like South Africa where reliable power is crucial. They transform mechanical energy—often from turbines or engines—into electrical power. This conversion fuels industries, homes, and essential services. Their applications span from small portable units to massive power plants. Sometimes, their roles even overlap, such as in hybrid systems where energy recovery is optimized. Knowing what are electric motors and generators helps us appreciate the intricate engineering supporting our daily lives and the sustainable future we all share.
Key Differences
Understanding the key differences between electric motors and generators reveals their unique roles in our daily lives. While both devices operate on the principles of electromagnetic induction, their functions are essentially opposite. An electric motor transforms electrical energy into mechanical motion, powering everything from household appliances to industrial machinery. Meanwhile, a generator converts mechanical energy back into electrical power, ensuring homes and industries stay connected to the energy they rely on.
One simple way to grasp their distinction is through their primary purpose. Electric motors are the silent engines behind mobility and automation, while generators serve as the vital source of electricity in times of power outages or in remote areas. For example, in rural South Africa, portable generators can mean the difference between work and stagnation. To clarify further, here’s a quick comparison:
- Electric motors use electrical energy to produce movement.
- Generators use mechanical energy to produce electrical power.
By understanding what are electric motors and generators, we gain insight into their vital contributions—each a testament to human ingenuity and resilience. Their differences are what keep our world running smoothly, whether in bustling cities or quiet rural communities.
Benefits and Importance of Electric Motors and Generators
Efficiency and Sustainability
Electric motors and generators are at the heart of modern energy systems, fueling industries, homes, and transportation in South Africa. Their efficiency directly impacts sustainability, reducing energy waste and lowering costs. When well-designed and maintained, these machines can operate with minimal energy loss, making them crucial for greener, more sustainable practices.
The importance of understanding what are electric motors and generators lies in their ability to optimize energy use. For instance, high-efficiency electric motors can significantly cut electricity consumption, which is vital given South Africa’s energy challenges. Similarly, reliable generators ensure continuous power supply during outages, safeguarding economic stability.
- Reduced environmental impact through lower emissions
- Cost savings for industries and consumers
- Enhanced energy security and resilience
In a landscape where energy efficiency and sustainability are more critical than ever, mastering the role of electric motors and generators becomes essential. Their innovative potential can lead to smarter, more responsible energy consumption that benefits both the economy and the environment.
Role in Renewable Energy
Electric motors and generators are pivotal in advancing South Africa’s renewable energy landscape. Their role extends beyond simple power conversion; they are the backbone of innovative sustainable solutions. For example, electric motors drive wind turbines and solar tracking systems, optimizing energy capture from natural sources. Meanwhile, generators provide essential backup during intermittent renewable energy production, ensuring a stable supply.
Understanding what are electric motors and generators is crucial for appreciating their benefits in renewable energy. They enable efficient energy conversion, reduce reliance on fossil fuels, and minimize emissions. As South Africa continues to embrace cleaner energy, these machines are increasingly central to efforts aimed at reducing carbon footprints and fostering energy independence.
- Enhanced energy efficiency
- Lower environmental impact
- Increased resilience in power systems
Impact on Modern Technology
Electric motors and generators form the silent backbone of modern innovation, transforming raw energy into motion and vitality. Their significance extends far beyond simple mechanics; they are the catalysts of progress, powering everything from industrial machinery to household appliances. In South Africa’s pursuit of a sustainable future, understanding what are electric motors and generators is essential, as they unlock cleaner, more efficient energy solutions.
The benefits of these machines are profound. Electric motors enhance energy efficiency in countless sectors, reducing waste and lowering operational costs. Meanwhile, generators ensure resilience by providing reliable backup power, especially crucial during unpredictable renewable energy fluctuations. Their impact on modern technology is undeniable, facilitating advances that are both environmentally responsible and economically vital. As the nation embraces greener energy initiatives, electric motors and generators are poised to revolutionize the way energy is harnessed and utilized, shaping a resilient and sustainable South Africa.