What is an Electric Motor?
Definition of an Electric Motor – Explaining what an electric motor is in simple terms
Imagine a tiny engine that can make things move without needing fuel or batteries — that’s what an electric motor does! An electric motor is a device that transforms electrical energy into mechanical energy, allowing machines to turn, spin, or lift objects. It’s like magic that powers many everyday items, from fans to electric cars. When electricity flows through the motor, it creates a magnetic field that pushes and pulls on parts inside, causing them to spin or move.
Understanding electric motors explained for kids is fascinating because it reveals how simple principles of magnetism and electricity work together. You might not see it, but inside many household appliances and vehicles, tiny electric motors are hard at work. For example, the motor in a toy car makes it zoom around, thanks to this clever technology. It’s amazing how such a small device can do so much—turning electrical power into motion that we can see and use every day!
Everyday Uses of Electric Motors – Examples of electric motors in toys, appliances, and vehicles
Electric motors are everywhere, quietly powering the world around us. From the tiny devices in your home to the massive engines in vehicles, these marvels of engineering make modern life possible. Electric motors explained for kids reveal how such small devices can turn electrical energy into the movement we see and feel, making everyday activities more fun and efficient.
In our daily lives, electric motors are found in many familiar objects. For example, the motor inside a blender whirs to blend your favorite fruit, or the one in a hairdryer creates the warm air we use to dry our hair. These motors are also crucial in transportation—electric cars rely heavily on electric motors that provide smooth, quiet power, helping to reduce pollution. The marvel of electric motors explained for kids isn’t just about how they work, but how they help us live better and more sustainably.
Here are some common everyday uses of electric motors:
- Toys, such as remote-controlled cars and drones, which move thanks to tiny electric motors.
- Home appliances like washing machines, refrigerators, and fans that use electric motors to operate efficiently.
- Vehicles, especially electric cars and bikes, that depend on electric motors for propulsion, offering cleaner transportation options.
How Does an Electric Motor Work?
Basic Principles of Magnetism – Introducing magnets and their forces
Imagine a tiny superhero inside your gadgets, turning electricity into motion—sounds like magic, right? Well, it’s actually science at work! Electric motors explained for kids reveal that these marvels rely on the fascinating principles of magnetism. When electricity flows through a wire coil inside the motor, it creates a magnetic field, turning the motor’s armature into a mini magnet. This is where the real fun begins: magnetic forces push and pull, causing the motor to spin and power everything from toys to washing machines.
Now, here’s a nifty fact—magnets have a special kind of force called magnetism, which makes things stick together or repel each other. This invisible force is the secret sauce behind electric motors. To understand how they work, think of the motor as a dance between two magnetic poles: north and south. When electricity energizes the coil, it produces a magnetic field that interacts with a permanent magnet, creating motion. The clever part? The motor switches the magnetic poles constantly, keeping the dance going and making things turn smoothly.
Creating Movement with Electricity – How electricity makes magnets move
In the shadowy realm where electricity and magnetism entwine, the workings of an electric motor become a captivating dance of unseen forces. Imagine a whispering current coursing through a wire, conjuring a magnetic field that commands the very fabric of motion. This is the essence of electric motors explained for kids—an elegant symphony of science and magic. When electric current flows, it energizes a coil, transforming it into a magnet with a north and south pole. The interaction with a fixed magnet then ignites a push and pull, causing the rotor to spin with relentless purpose.
To grasp this mysterious process, picture the motor’s core as a battleground of magnetic poles—like a duel between invisible giants. As the electric current switches direction, it flips the poles, ensuring the motion never ceases. The result? An endless waltz powered purely by electricity. This continuous switching is what makes electric motors explained for kids so enchanting—each turn a testament to the invisible forces shaping our world.
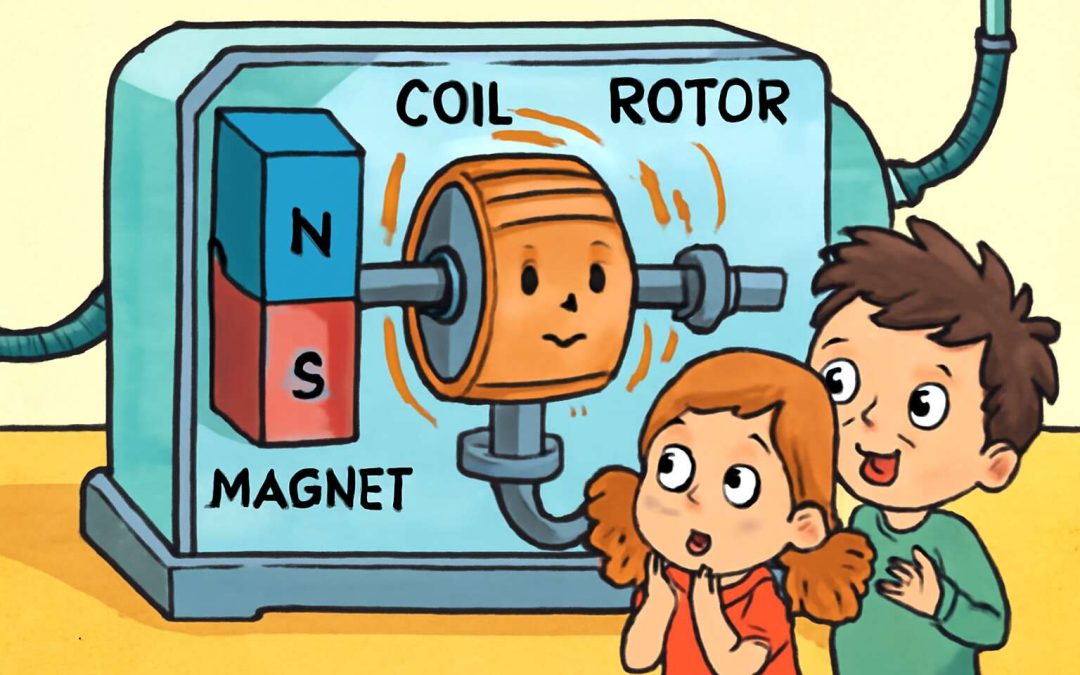
Parts of an Electric Motor – Stator, rotor, magnets, and wires
At the heart of every electric motor lies a delicate yet powerful assembly of parts that work in harmony to produce motion. These components—stator, rotor, magnets, and wires—each play a vital role in transforming electrical energy into mechanical movement. Understanding how they fit together reveals the silent poetry behind modern machinery, a symphony of science and engineering.
The stator is the stationary part of the motor, often wrapped in coils of wire. When electricity flows through these wires, it creates a magnetic field that energizes the stator. Opposite this is the rotor, a spinning component that reacts to the magnetic forces. Magnets—either permanent or electromagnets—are strategically placed to interact with these fields, pulling and pushing the rotor with relentless energy. The wires, carefully arranged, carry the electric current, switching directions to keep the motor spinning smoothly.
In electric motors explained for kids, the magic unfolds through a simple yet intricate dance of magnetic poles. The process can be summarized in a few steps:
- The electric current energizes the stator coils, creating a magnetic field.
- This magnetic field interacts with the magnets on the rotor, causing it to turn.
- Switching the current’s direction ensures the rotor keeps spinning without stopping.
Every part of an electric motor works together to produce the continuous, mesmerizing motion we often take for granted—yet it all begins with these tiny, unseen forces working behind the scenes. Electric motors explained for kids reveal not just a machine, but a glimpse into the elegant dance of magnetism and electricity shaping our everyday world.
Types of Electric Motors
D.C. Motors – Motors powered by direct current
When exploring electric motors explained for kids, it’s fascinating to see how versatile these devices are. Among the various types, D.C. motors—short for direct current motors—stand out for their simplicity and widespread use. These motors are powered by direct current, meaning electricity flows in one steady direction, allowing precise control over the motor’s speed and direction. This makes D.C. motors ideal for small gadgets, toys, and even electric vehicles!
What truly makes D.C. motors captivating is their straightforward design. They often feature a commutator and brushes that work together to keep the motor spinning smoothly. Here’s a quick overview of their common types:
- Brushed D.C. motors—classic and easy to understand, perfect for beginner projects.
- Brushless D.C. motors—more efficient and durable, used in high-tech gadgets and drones.
In the realm of electric motors explained for kids, understanding D.C. motors reveals how electricity transforms into motion—an elegant dance of magnetism and engineering that powers much of modern life in South Africa and beyond!
A.C. Motors – Motors powered by alternating current
As the sun rises over South Africa’s vibrant landscapes, a quiet revolution hums beneath our everyday lives—powered by the unseen force of electric motors. These marvels of engineering, often invisible yet indispensable, transform electricity into motion with a symphony of magnetic forces. While D.C. motors have their charm, the realm of electric motors explained for kids also encompasses the dynamic world of A.C. motors—machines that dance to the rhythm of alternating current.
A.C. motors operate on a different principle, where the electric current shifts direction many times each second, creating a perpetual wave of energy. This oscillating nature allows them to power large appliances, industrial machines, and even the fans we use to cool our homes. Their design often involves a stator—a stationary part that generates magnetic fields—and a rotor that spins in response. It’s as if the motor breathes in and out with the rhythm of the power supply, turning electrical pulses into a smooth, continuous motion.
- Induction motors—robust and efficient, perfect for factories and large-scale operations.
- Synchronous motors—precise and reliable, ideal for timing-sensitive applications.
Understanding electric motors explained for kids reveals how these devices, fueled by the alternating current flowing through our world, keep South Africa moving forward—powering everything from small fans to massive industrial giants with a quiet, relentless energy.
Simple Motors for Kids – Easy-to-understand examples and models
Electric motors come in many shapes and sizes, each designed to do specific jobs. For example, simple electric motors found in toys are small but mighty—turning batteries into spinning wheels or flashing lights. These miniature marvels show how electricity and magnetism work hand-in-hand to create movement. Kids often find these motors fascinating because they turn something as ordinary as a battery into an exciting, whirling device!
Another common type is the basic electric motor used in household appliances like fans or washing machines. These motors are cleverly built with parts like the stator and rotor, which work together to produce smooth motion. Understanding electric motors explained for kids reveals how these devices can be as simple as a toy or as complex as a large industrial machine.
Here’s a quick look at two main types of simple electric motors:
- Brushed motors—found in many toys, they use brushes to deliver electricity directly to the spinning part.
- Brushless motors—more efficient and durable, often used in drones and electric vehicles.
These variations showcase how electric motors explained for kids can be both fun and functional, powering a world that’s constantly moving forward with unseen but vital energy!
How Electric Motors Are Made
Materials Used – Wires, magnets, and other components
Imagine tiny, powerful engines working quietly inside your favorite toys and appliances—these are electric motors! To craft these marvels, engineers use a carefully chosen selection of materials that work together in perfect harmony. Wires, often made of copper or aluminum, are the lifelines that carry electric current into the motor, acting like tiny roads guiding power right to where it’s needed. Magnets, which can be made from rare earth elements or iron, are the secret to creating the magnetic forces that make the motor spin with energy. Other components include the stator and rotor—these are the heart of the motor—wrapped in insulating materials to keep everything safe and efficient.
- Magnetic materials like neodymium or ferrite
- Insulating materials to prevent short circuits
- Bearings for smooth rotation
These parts work together in a magical dance, transforming electrical energy into the movement that powers everything from electric cars to small household gadgets. Electric motors explained for kids reveals a world where science turns into wonder, spinning simple materials into extraordinary motion!
Assembly Process – Basic steps to build a simple electric motor
Building an electric motor is like assembling a tiny, powerful magician’s device—each step carefully crafted to turn electricity into motion. The assembly process begins with the core components: the stator and rotor, which are the heart of the motor. These parts are made with magnetic materials like neodymium or ferrite, chosen for their superpower to produce strong magnetic forces. Next, wires—usually copper or aluminum—are wrapped around the rotor to create electromagnetic fields that respond to the stator’s magnets. This is where the magic starts to happen, as electricity flows through these wires, generating the magnetic forces needed to spin the rotor.
To keep everything running smoothly and safely, insulators are added to prevent short circuits, and bearings are installed to allow the rotor to spin effortlessly. For a simple electric motor explained for kids, the assembly can be summarized in these basic steps:
- Attach the magnets to the stator securely.
- Wind the copper wires around the rotor to form coils.
- Insert the rotor into the stator, ensuring the bearings are in place for smooth rotation.
- Connect the wires to a power source, like a battery or small circuit.
And just like that, a basic electric motor is born—ready to turn electrical energy into the spinning motion that powers countless everyday gadgets. In the world of electric motors explained for kids, this process reveals how simple materials come together in a dance of science and wonder, creating energy that moves the world around us!
Fun Facts About Electric Motors
Interesting Facts – Cool trivia about electric motors
Electric motors are like tiny wizards that turn electricity into motion, powering everything from toys to giant machinery. But did you know that the first electric motor was invented over 150 years ago and has since become an essential part of modern life? These marvels operate silently and efficiently, transforming magnetic forces into the movement we see and feel every day.
One fascinating fact about electric motors explained for kids is their hidden connection to magnets. Inside each motor, powerful magnets and coiled wires dance together, creating a magnetic field that pushes and pulls to generate rotation. This dance of forces is so precise that it can make a small fan spin or a car’s electric engine roar to life! The magic lies in the seamless interplay of electricity and magnetism, turning simple components into a symphony of motion.
- Electric motors are used in almost every modern device, from your favorite toys to electric vehicles.
- The largest electric motor in the world can generate enough power to light up a small town!
- Some electric motors are so tiny that they can fit inside a watch or a medical device, working quietly and efficiently.
Electric Motors in Space – How electric motors help in rockets and satellites
Electric motors have a surprising role beyond our everyday gadgets—they are the silent heroes propelling humanity into the future of space exploration. In the vast darkness of space, where traditional engines falter, electric motors explained for kids reveal their true power. These marvels are at the heart of rockets and satellites, transforming electric energy into the precise movements needed to navigate the cosmos. Without them, the marvels of modern space travel would be impossible.
Imagine tiny yet mighty motors working tirelessly to control satellite orientation or to adjust the position of space telescopes. Their compact size and reliability make them perfect for such demanding environments. In fact, some of the most advanced electric motors in space are so efficient they can operate in the vacuum of space without missing a beat. It’s almost poetic how these small components help us reach for the stars, demonstrating the incredible potential of electric motors explained for kids in the most awe-inspiring ways.
Why Are Electric Motors Important?
Environmental Benefits – Electric motors are cleaner and more efficient
Electric motors play a crucial role in our daily lives, helping to power everything from small gadgets to large machines. One of the most exciting aspects of electric motors explained for kids is understanding their environmental benefits. Unlike traditional engines that burn fuel and release harmful gases, electric motors are much cleaner. They produce no exhaust and operate quietly, making them better for our planet and our communities.
Moreover, electric motors are highly efficient, meaning they convert most of the electricity they use into useful movement. This efficiency helps reduce energy waste and lowers electricity bills. As more renewable energy sources like solar power are used, electric motors become even more environmentally friendly, supporting a greener future for South Africa and beyond. Their ability to cut down on pollution while still powering our homes, cars, and industries makes electric motors an essential part of sustainable development.
Innovations and Future Uses – New technologies using electric motors
Electric motors are not just the engines behind your favorite gadgets—they are the future of innovation! As technology evolves, electric motors continue to unlock exciting possibilities. Imagine a world where our cars, robots, and even household appliances run entirely on electricity—sounds like sci-fi, but it’s rapidly becoming reality. Their importance is growing, especially in South Africa, where sustainable energy solutions are vital for a greener tomorrow.
One reason electric motors are so important is their role in advancing renewable energy use. New technologies leveraging electric motors are making solar-powered vehicles and energy-efficient machinery more accessible than ever. For example, electric motors explained for kids often highlight how these devices are at the heart of electric cars, which produce zero emissions and help reduce pollution. As innovation accelerates, we’re seeing electric motors integrated into smart grids, drones, and even underwater exploration devices!
These innovations are not just cool—they’re crucial. Electric motors are enabling us to develop more sustainable solutions that benefit both the environment and the economy. In South Africa, where energy challenges are prominent, electric motors powered by renewable sources are helping to transform industries and transportation. Their ability to adapt and improve ensures electric motors will remain a key player in future technological advancements.